Introduction:
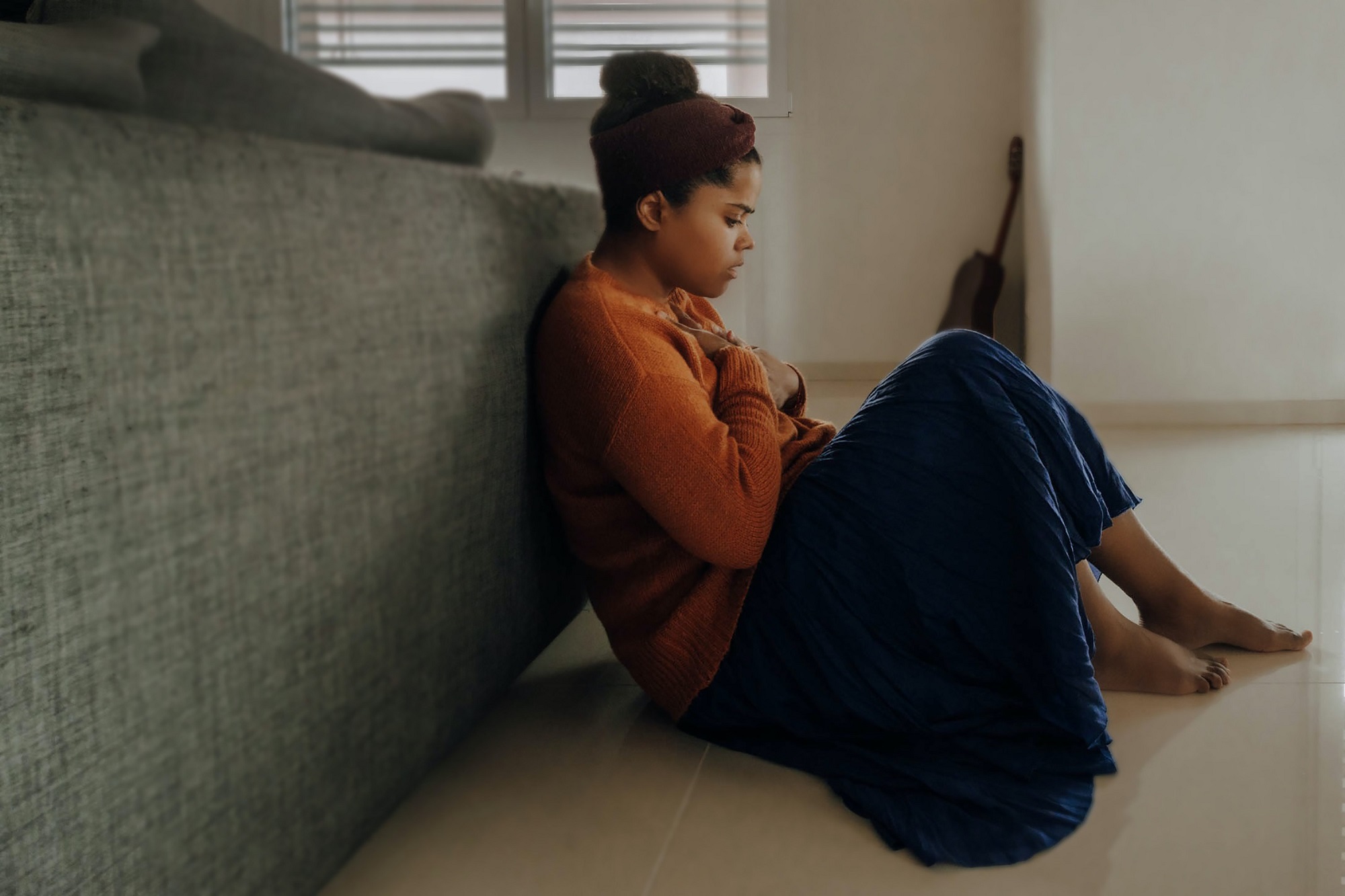
Postpartum depression (PPD) is a significant mental health condition that affects around 1 in 7 new mothers. It is a form of clinical depression that occurs after childbirth and can bring about a range of symptoms. This article explores the symptoms, treatment options, and the importance of support for coping with postpartum depression. By shedding light on this topic, we aim to increase awareness and provide guidance to those experiencing PPD.
Understanding Postpartum Depression:
Postpartum depression manifests in various symptoms that can significantly impact a mother’s well-being. These symptoms may include feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and worthlessness, loss of interest in once-enjoyable activities, sleep disturbances, changes in appetite or weight, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and even thoughts of self-harm or suicide. It is crucial to recognize these symptoms and seek appropriate help to ensure effective management of PPD.
Symptoms and Impact of PPD: Recognizing the Signs of Postpartum Depression
Postpartum depression presents a unique set of symptoms that distinguish it from the “baby blues” or general feelings of moodiness after childbirth. It is important to differentiate between these two conditions to provide appropriate support to those experiencing PPD. The symptoms of PPD can significantly impair a mother’s ability to care for herself and her newborn, and can strain relationships with partners and family members.
Seeking Treatment for PPD: Treatment Options for Postpartum Depression
Fortunately, effective treatments are available for postpartum depression, offering hope for recovery. It is important to approach treatment in a comprehensive manner, considering various approaches that address both the emotional and physical aspects of PPD.
Therapy: Talk therapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), has shown to be beneficial in treating PPD. CBT helps individuals identify negative thought patterns and develop coping strategies to manage their symptoms effectively. It provides a safe space to express emotions and work through the challenges associated with PPD.
Medication: In some cases, antidepressant medications may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms of PPD. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most suitable medication and dosage, taking into account the potential side effects and individual circumstances.
Self-Care Practices: Promoting Self-Care for Managing PPD
Engaging in self-care practices is an essential component of managing postpartum depression. Simple yet impactful activities can help improve well-being and support recovery. Prioritizing adequate sleep, maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and finding moments for relaxation and self-reflection can contribute to overall mental wellness during the postpartum period.
Building a Support Network: The Power of Support in Overcoming PPD
Having a strong support network is crucial for individuals coping with postpartum depression. Partners, family members, friends, and healthcare providers can offer emotional support, practical assistance, and understanding. Sharing experiences with other mothers who have gone through similar challenges can also provide a sense of belonging and reassurance. It is essential to communicate openly and seek help from loved ones and professionals to foster a supportive environment.
Conclusion:
Recognizing the signs of postnatal emotional distress, seeking suitable treatment, and establishing a strong support network are essential in managing this challenging phase. Canaan Healthcare Inc. is dedicated to delivering comprehensive mental health services, encompassing therapy and medication management, to aid individuals facing postnatal emotional challenges. Remember, reaching out for support is a brave and pivotal step towards healing. With the right care, support, and self-nurturing, individuals can navigate through this period and embrace a positive and fulfilling postpartum experience.